
What triggered these dramatic events, and what might they tell us about. Read the information about this extinction (formally known as the Cretaceous-Paleogene or sometimes the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction). Exploring Science Earth Science Weather and Climate. When were those intervals? It was very simple single-celled organisms. be used in support of Dan Schrag's 2012 Holiday Lecture on Science, Earth's Climate: Back to the Future. Some water may also have been brought to Earth by comets and asteroids. Use the CHART button to find an approximate temperature range for the three intervals. 12-14 Subduction of ocean sediments affect CO2 levels (26:57-30:32) lesson. How are deep ocean currents formed? 8 terms. Over the last 540 million years, icecaps covered at least one of the Earth's poles during three intervals. Additional layers let students explore changes in atmospheric composition, temperature.
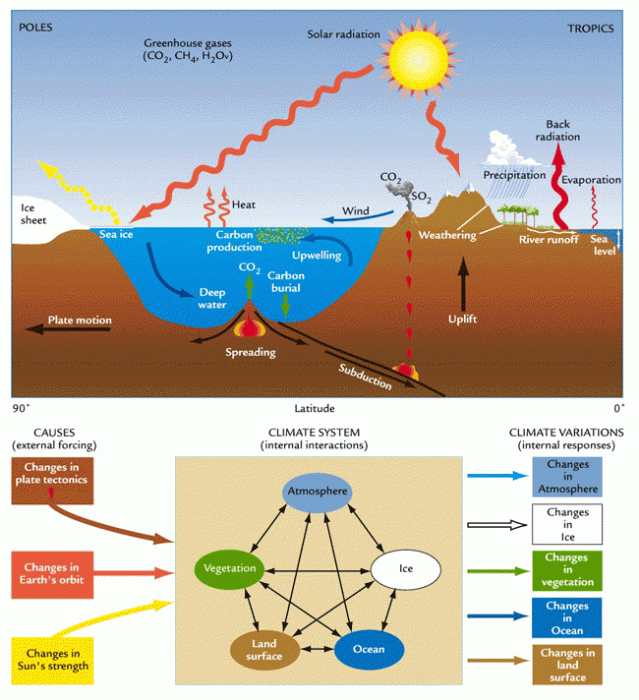
Click anywhere on earth to watch local video and a 360° street view. To switch between the three timelines, use the pinch or spread gesture Select "CHARTS" to. Use the silver slider to view the changing Earth through geologic time. Zoom in or out by pinching or spreading your fingers on the screen. This activity challenges students to provide their questions and ideas for experiments they could conduct to investigate the impact of releasing genetically modified mosquitoes into the wild. They then build a model of how carbon cycles through the Earth system. seasons (dependent on earth's tilt) annual insolation-temperature cycle: solar radiation highest on June 21st and lowest on December 21st (ocean has large heat capacity, land has small heat capacity) Annual Temperature Range→big over land, small over oceans big at poles, small at equator radiation imbalance at equator vs poles→winds and. biointeractive exploring earth's climate with earthviewer answer key. Spin the Earth with your finger to get a 360-degree view of the world. Transcribed image text: Exploring Earth's Climate with EarthViewer Tips for using the App. This activity guides students through building a conceptual model of how carbon dioxide affects Earth's climate.

They can "drop a pin" in any location to see historic climate data, detailed wildlife descriptions, stunning pictures, and more. HHMI Earth Viewer App Earth's Climate History (Then click "Launch Interactive") Considering the Evidence for Mass Extinctions and Exploring Earth's Climate with EarthViewer INTRODUCTION At least five times in Earth's past, the vast majority of plant and animal species have been annihilated in a geologic instant. Use the EarthViewer features to fill in the following chart. Students read a passage about the interaction of geology and the carbon cycle.
The information tells you that "overwhelming evidence suggests that the extinction was caused by a 10-km-diameter asteroid that struck Earth." It then cooled, fell back down as rain, and formed the Earth's first oceans. Causes of currents are: deep/density = temperature and salinity differences They can also explore global trends in natural features and human activities, including how patterns of human settlement and agriculture have changed the planet since 1700. Mass Extinctions in Earth History Student Worksheet Published April 2016 of 4 6.!Gather data: Drag the slider to the Ordovician extinction, 440 MYA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
